In this digital age, we are extremely reliant on data – and the amount of data companies are creating is continually increasing. While all this data is inevitable, it is useless unless companies gain insights and meaning from it – to gain tangible value in less time.
Historically, data analysis, app creation or automation would be achieved by IT/Development teams. This would require staff to outline their requirements and aims, submit these requests to their IT department (or even an external partner) and then see whether it was approved and subsequently, wait for it to be built. This would be time-consuming and would use valuable resources internally or be costly if fulfilled externally. What’re more, those requesting the solution would tend to have an immediate need and waiting for weeks could cause internal delays.
This is why the Power Platform is so exciting. The Power Platform enables data democratization – the ability for digital information to be accessible to the typical (non-technical) end user. It provides four technologies that allow staff to do more with their data themselves without coding knowledge. While it doesn’t allow the flexibility of custom coding, it does provide a simple method for most users to be able to create, automate or analyze their data in ways which have never been possible for the average worker.
What is the Power Platform?
“Power Platform is a low code platform offering provided from Microsoft which spans Office 365, Azure, Dynamics 365 and standalone applications.”
Power Platform combines the robust power of PowerApps, PowerBI, Power Automate and Power Virtual Agents into one powerful business application platform — providing Act, Automate, Analyze and chat bots ability to build business application. The Power Platform is possible thanks to the Common Data Service for Apps(CDS), which is essentially the underlying data platform that provides a unified and simplified data schema so that applications and services can inter-operate.

Power Platform Products:
The Power Platform enables the ability for digital information to be accessible to the typical (non-technical) end user.
Power Platform is comprised of four key products:
- Power Apps
- Power Automate
- Power BI
- Power Virtual Agents
Power Apps:
It is a rapid low code development environment for building custom apps for business needs. It provides services, connectors, and a scalable data service and app platform (Common Data Service) to allow simple integration and interaction with existing data. Power Apps helps you build and deploy customized apps that work across web and mobile, embedded or standalone, on any device. All you have to do is to go to Power Apps and start building your own app as per the requirements. You need an office 365 subscription in order to get the power apps facility free.
Both developers and non-developers can create apps within PowerApps as it works in a no-code or low code environment. However, more technical users are able to extend capabilities by using Azure functions or creating custom connectors and integrated solutions.
- Build scalable and responsive apps which can run on web, mobile, tablet or any other device without No Code.
- Connect to and harness data from your business applications, such as Dynamics 365 and Office 365 (and also third-party apps).
- Build apps used for internal users or websites for external facing customers.
- Build apps from an existing data set with a predefined template.
With Power Apps, following types of Apps can be created:
- Model Driven Apps
- Canvas Apps
- Portals Apps
Power Automate:
Power Automate was previosly known as Microsoft Flow. This allows you to create automated workflows between Applications, Services and other third-party applications, which allows to avoid carrying out repetitive tasks and save valuable time.
For an example, imagine you upload video to Youtube daily and share that on twitter and facebook each time you upload. This process can be automated using power automate so that once you upload the video, an action will be triggered to share it in social media. For another example, imagine you want make a purchase for the organization once you make the request ,the manager has to accept/reject so that you can proceed through the process. This flow of getting approval from the manager once you make the request and the actions taken posterior can be automated as follows.
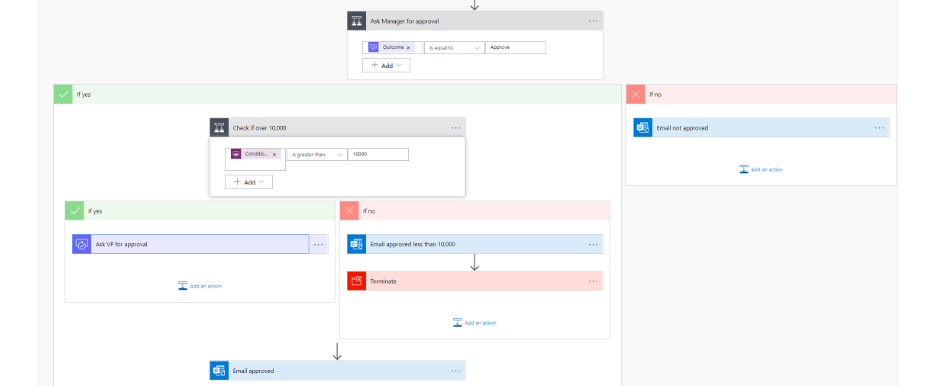
- Use pre-built automation templates for common business process automations
- Set up triggers, alerts, automated emails, push notifications, automating of repetitive tasks like moving data from one system to another and much more — with no coding and in minutes.
- Guiding a user through a process so they can complete the different stages
- Create automations by connecting various applications and external data sources, such as Outlook, SharePoint, Dynamics 365 or non-Microsoft apps like Twitter, Asana, Gmail, MailChimp etc via one of the hundreds of connectors or directly via an API
Power BI:
PowerBI is a business analytics service provided by Microsoft. Using data stored in CDS or other databases, users can build informative reports and dashboards to display important data about sales, customer service, and other business functions. These dashboards and reports can be published on websites, in SharePoint or Teams, and in Apps.
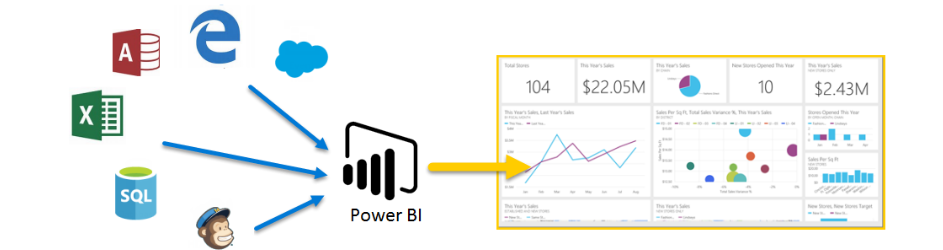
Power BI is a business analytics tool which allows you to easily connect to data sources, create visuals and gain business intelligence quickly. It allows you to:
- Click and connect with Microsoft and third-party cloud services, as well as on-premise data sources
- Easily manipulate data and create visuals, such as charts, dashboards, maps and many more — so you can present your data in an easy-to-digest format
Power Virtual Agents:
Power Virtual Agents empowers developers to easily create powerful bots using a guided, no-code graphical interface without the need for data scientists or developers.
It eliminates the gap between the subject matter experts and the development teams building the bots. It removes the complexity of exposing teams to the nuances of conversational AI and the need to write complex code. And, it minimizes the IT effort required to deploy and maintain a custom conversational solution.
Using Power Virtual Agents, you can:
- Empower your teams by allowing them to easily build bots themselves without needing intermediaries, or coding or AI expertise.
- Reduce costs by easily automating common inquiries and freeing human agent time to deal with more complex issues.
- Improve customer satisfaction by allowing customers to self-help and resolve issues quickly 24/7 using rich personalized bot conversations.
The beauty of power platform is that each of these four key products, power apps, power automate, power BI and virtual agents can be used interactively together. For an example, you can trigger an automated flow once you press a button in your power app. Or you can preview a visualization obtained from power BI in your power app. You can also add a chat bot created from power virtual agent in your power portal created.
Power Platform Architecture:
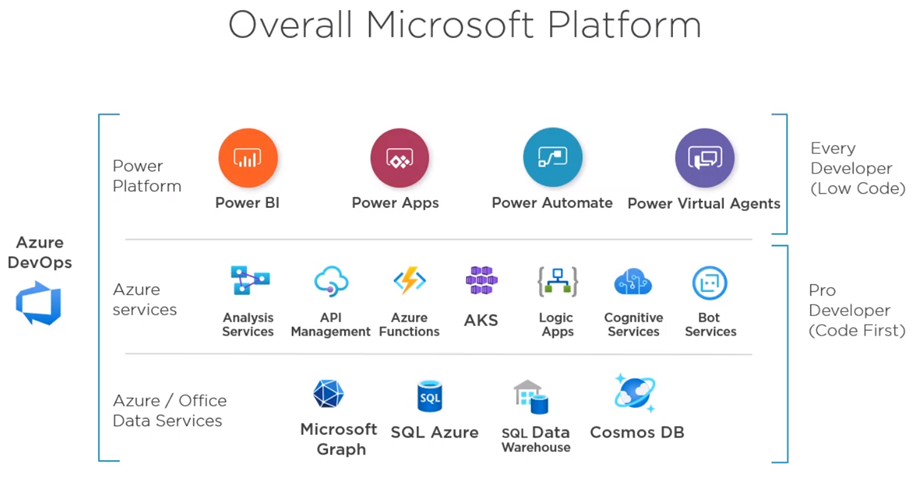
Power Platform itself is divided into multiple components and layers where each component is dynamic and scalable by itself, but brilliant and masterful when combined. From a developer or more precisely citizen developer’s perspective, Power Platform is splited into Power Apps, Power BI, Power Automate and Power Virtual Agents, which be used to map their business process requirements.
This platform is build upon lots of services which powers this platform and Pro Developers can interact with these services also in order to perform advance functionalities. Common Data Service (Apps) is harnessed from Azure Data services like Azure SQL, Cosmos DB, Blob Storage etc. Similarly Azure API management service is involved in integrating all of the products with API management. Bot Services powers Power Virtual Agents wheres Analysis Services powers Power BI.
Common Data Service (CDS)
The heart of the Microsoft Power Platform is the Common Data Service for Apps(CDS). It is a central data repository for business data.
CDS is a secure database hosted in Azure Cloud prebuilt with a standard set of entities and record types. These record types — for example, Accounts, Contacts, and various activity types are extensible — so you can add additional data fields. Developers can also add new entities to fit their business needs. Entities have relationships to each other, and Business Rules can be created to make fields required, to hide fields and to set default values.
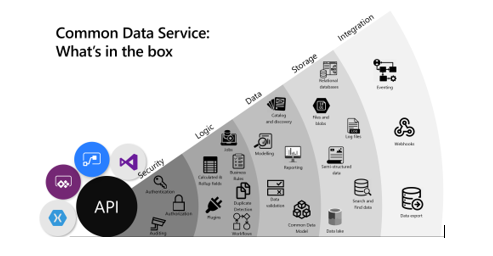
Common Data Service offers following categories of functionality:
- Security Common Data Service handles authentication with Azure Active Directory (AAD) to allow for conditional access and multi-factor authentication. It supports authorization down to the row and field level and provides rich auditing capabilities.
- Logic Common Data Service allows you to easily apply business logic at the data level. These rules could be related to duplicate detection, business rules, workflows, or more.
- Data Common Data Service offers you the control to shape your data, allowing you to discover, model, validate, and report on your data. This control ensures your data looks the way you want regardless of how it is used.
- Storage Common Data Service stores your physical data in the Azure cloud.
- Integration Common Data Service connects in different ways to support your business needs. APIs, webhooks, eventing, and data exports give you flexibility to get data in and out.
Important things to consider before using power platform
- Power apps you created cannot be shared with the outside world but within your organization. They are not for consumer-consumption
- Since this is almost a no-code platform, developers cannot add any HTML or JavaScript code scripts to add/change any feature. Simply, if power apps cannot provide a particular feature, developer can’t too.
- But if you need any custom logic that power apps platform cannot provide, the best option is to connect it to any custom API. (The platform allows you to connect to any external APIs.)
- Less interference from the developers has increased the stability and long term use.
- Although you don’t require a coding experience to use the power platform, you must be able to write formulae (In DAX) in order to describe your logic.
- Any type of data (XML, JSON, Excel, SQL, data from google analytics) can be used within power platform.
- Visualization and reports from PowerBI can be embedded in any external application.
- Functionality of power platform sometimes may not meet your requirements. But Microsoft is regularly adding new features and updating to ease your day to day tasks in your organization.
References
- https://powerplatform.microsoft.com/en-us/
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/powerplatform/